Starting your own venture in Canada can open the door to independence and long-term success. It gives you control over your work, the chance to build wealth, and the opportunity to contribute to your community.
At the same time, starting a business in Canada takes effort and persistence. According to Key Small Business Statistics, many small companies struggle in the first few years, and only those with strong planning and commitment continue to grow.
The encouraging part is that thousands of entrepreneurs have already gone through company registration in Canada and proven that success is possible. By following the right steps and preparing carefully, you can turn your idea into a real business. If you plan to hire early, working with trusted EOR companies in Canada can also help simplify initial employment and compliance tasks.
This guide and checklist, supported by resources from BDC, will walk you through the process from the ground up, so you understand exactly how to register, launch, and manage your company with confidence.
Business Idea

It is always best to verify that your idea is viable before you waste time or money in establishing your company. Canada has a competitive market, and only those who are well prepared shine. When starting a business in Canada, the first question you should ask yourself is:
- Why is your company unique among your existing competitors?
- Who are your specific target customers, and what is the problem that you will solve for them?
- What sum of money will you require, and how do you acquire it most effectively?
Investing time in this research at this moment can save you unnecessary expenses in the future. Healthy market validation also ensures that you are sure to proceed with company registration in Canada.
Test your idea both online and offline. Online tools such as Google Trends may indicate changes in demand, and platforms such as SurveyMonkey or Typeform may enable you to gather direct feedback from potential customers. Speaking of competitors, you can refer to such a market analysis tool as SimilarWeb or SEMrush to gain some insight into the way they attract and serve customers.
The best method to launch a small business is usually to prove an idea right, and the steps to transform initial ideas into profitable businesses are posted in Quick Way to Launch Small Businesses.
Start with Market Research

Before pouring resources into building your product or service, begin by validating your market. Solid market research helps you find a profitable niche, understand consumer behavior, and see where your company can make a real impact.
Your steps might include:
- Identify your ideal customers: demographics, behaviors, needs.
- There will be a knowledge gap regarding what they desire, grieve, and where existing solutions have failed.
- Chart out your competition, their strengths and weaknesses and any gaps that they leave open.
- Integrate both primary and secondary data including industry reports and public statistics along with surveys, interviews and focus groups.
Your goal is to achieve product market fit, where people not only buy from you but also become advocates.
Canada has great resources for this. Check out Statistics Canada’s Small Business Hub, a central portal with economic data, sector trends, and resources for new and existing entrepreneurs.
Also, studies in Canada show that small businesses with 1 to 19 employees make up 86.7% of all employer firms.
For tools that simplify this process, consider AI market research tools to help you gather insights faster.
One of the best ways to launch small business is by starting from deep research and then shaping your offering around what your market truly needs.
Plan Your Financing Options

Consider how you will get the money required to start and maintain your business before you dive into operations. There are numerous opportunities in Canada, including individual savings and family loans, bank loans, credit unions, and government-assisted financing schemes. There has also been the emergence of crowdfunding sites and angel investors, who provide startups with the chance to test their ideas and raise funds.
The correct choice will be determined by your vision. As an illustration, venture capital or issuing shares may be reasonable should you wish to open a company in Canada as a corporation with national ambitions. When you are small, a micro-loan or personal credit line would suffice as a sole proprietor. All you need to do is select a financing route that suits your ambitions and maintains your risk levels manageable.
Build Guidance Into Your Journey

Money will not protect your company. It is always better to have an experienced person to show you the right path. The mentor can assist in your strategic decisions, customer acquisition, and even crucial steps such as the business name registration in Canada, which is essential to credibility.
Futurpreneur Canada matches young entrepreneurs with mentors who give them real-world advice to help them grow their business. Beyond formal programs, you may also be able to network in industry associations, local chambers of commerce, or online communities of entrepreneurs to get good mentorship.
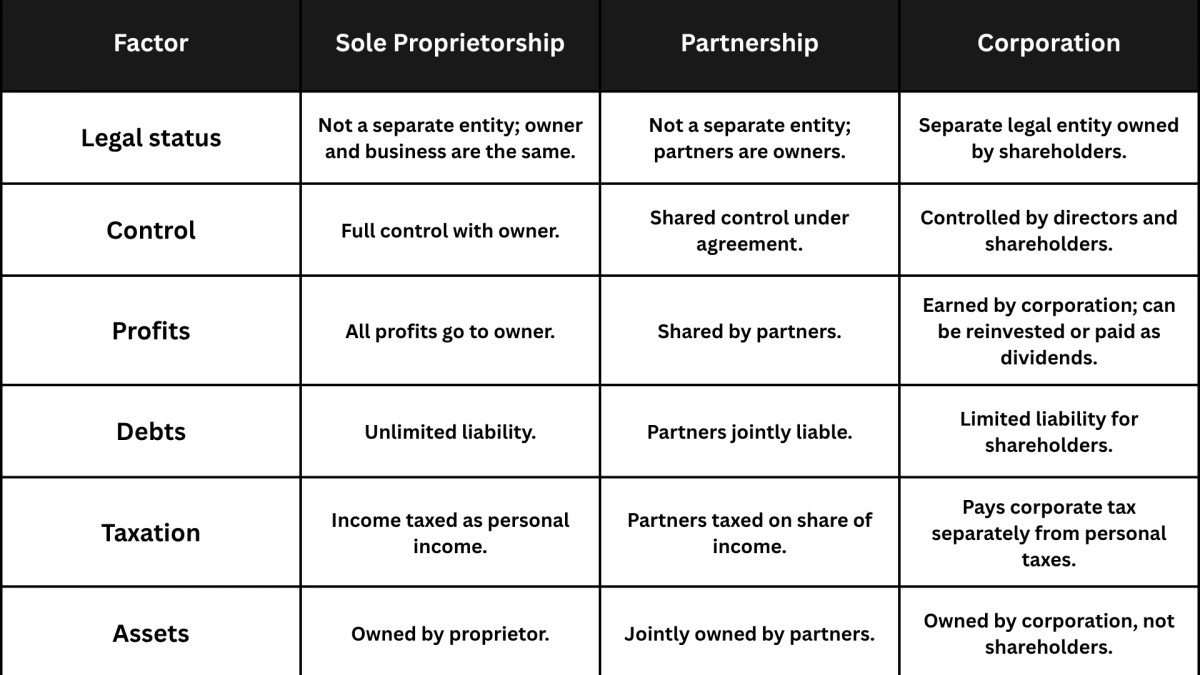
Choose the Right Business Structure

The choice of legal form for your company is one of the most significant ones when starting a business in Canada. This option impacts taxes, liability, and money raising. Three structures are to be considered:
Sole Proprietorship
The most common and simplest type of structure is for small businesses. Simple and cheap to install, and the income is claimed on your personal tax filing. The disadvantage is indefinite liability, where you yourself are liable for debts and risks.
Partnership
A partnership has much in common with a sole proprietorship, yet includes two or more individuals. Business partners tend to enter into a contract that provides a way of sharing profits, costs and liabilities. The power of pooling resources can be great, and all partners can be party to the actions of others.
Corporation
A corporation is a legal entity. This implies that shareholders will be at little risk, tax benefits may be incurred, and they will be trusted more in the market. Financing may also be easier to reach once incorporated. Conversely, it involves increased set-up costs, less paperwork and continuous reporting requirements.
You may be federally/provincially incorporated. Federal incorporation enables you to use your company name throughout Canada, whereas provincial incorporation only protects your name in one province.
Pros and Cons of Business Structures
Steps to Register a Corporation in Canada

In case you intend to register a company in Canada as a corporation, there are several steps that need to be followed. Every step will make sure the business is legal and in compliance nationwide.
Choose your incorporation type
You may either incorporate federally or provincially/territorally. Federal incorporation enables you to carry your business name in all of Canada, whereas provincial incorporation gives you business name rights in only one province or territory.
Obtain your business number and tax accounts
Once you have been incorporated, you will be required to obtain a business number and a corporation income tax account with the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA). This is to make sure that your company is prepared to be under the rules of company registration Canada to pay taxes.
Register extra-provincially if needed
When you have incorporated in one province and intend to operate in other provinces or in other territories, you will also have to register as an extra-provincial (or extra-territorial) corporation in those provisions.
For complete instructions, visit the official guide on Registering a Corporation in Canada.
Taxes and Start-Ups

If you are starting a business in Canada, you must also be ready to meet your tax responsibilities. Among the conditions is the necessity to register GST/HST in case:
- You offer taxable goods or services in Canada.
- In one calendar quarter or four quarters in a row, your total taxable revenues are more than 30,000.
In addition to sales tax, you are required to submit an income tax return during your first financial year. Precisely the rules differ according to the province or territory in which you are operating, and federal laws. To prevent errors, many business people employ the services of a professional accountant at the beginning. The Canada Revenue agency also offers free services to small businesses and self-employed people to help them know what to do.
Choose a Business Name

The name of your company will be the first thing that customers will see on you, therefore it must be accurate, memorable and available. Brainstorming might be a difficult task, and faster and more creative results are possible with the help of a business name generator.
When choosing your name, ask yourself:
- Does it reflect the qualities of my products or services?
- Is it easy for customers to remember?
- Is it unique and different from existing names?
Legally, you name must not be similar or similar to that of another registered corporate name or trademark. This implies that it must be carefully searched and then finalized. In the case of most businesses, business name registration Canada is a required process, but there is an exception of sole proprietorships being filled with the legal name of the owner.
Lastly, remember that your name should also be a web domain name where customers can find you online easily. Selecting the right name is not only a branding exercise but also a foundation for how to establish a company in Canada with long-term credibility.
Obtaining a Business Licence

You may require licences or permits before you can legally start depending on what kind of company you run. Different industries and places have different requirements and it is always best to check with your province, territory, or local municipality. The online BizPaL tool is also useful and helps the entrepreneur find what permits and licences they require in Canada. This step is crucial for compliance when you plan to register a Canadian company.
Intellectual Property Protection

Your business can be made up of ideas, products, or inventions that require protection by law. Otherwise, others will imitate your work or brand identity. Intellectual property (IP) covers trademarks, patents, industrial designs and copyright.
To learn how to secure your IP, visit the Canadian Intellectual Property Office (CIPO). The registration of trademarks and patents can give your business exclusive rights that create long-term value.
Put Together a Business Plan

At this stage, you have made some crucial steps towards starting a company in Canada. The second step is to prepare a full business plan. This paper contains your vision, plans and financial projection. A good business plan not only gets you focused but also makes you professional in the eyes of banks and investors.
The main components of a business plan are:
- Market research: An overview of the competitions of your products and brand.
- Executive summary: An overview of your business plan.
- Company profile and mission: Products, services, target markets and industry trends.
- Sales and marketing plan: Customer profiles, pricing, advertising and distribution.
- Operations plan: Places, equipment, technology, and production techniques.
- Human resources plan: Staff, recruiting, training and retention.
- Action plan: Growth milestones and growth timelines.
- Financial plan: Budgets, sales projections, costs and cash flow estimates.
To help you, the Government of Canada offers a step-by-step business plan guide, which is also free, and you can also use the templates available on the site and tailor them to your purposes.
Prepare an Elevator Pitch

Not all investors or partners can spare 20 pages to read a document. That is why you too ought to come up with a convincing, well-crafted elevator pitch. You should be in a position to discuss what your business does, what is special about it and why it can grow within 60 to 90 seconds. A pitch opens the door to financing, partnership and new customers.
Finance Your New Business

Bootstrapping: Most entrepreneurs start by funding their businesses out of their own savings. However, as your business expands you might need outside capital.
The two key forms of finance include:
- Debt financing: Banks or other financial institutions' loans that are subject to interest.
- Equity financing: Investor money, e.g. angel investors or venture capitalists, in consideration of ownership shares.
Main Sources of Financing for Start-ups
- Personal investment: Using your own funds shows commitment and builds credibility with lenders.
- Family and friends (love money): A common but sensitive source, often called patient capital.
- Business loans: Banks and credit unions remain the most common lenders. Explore government programs like the Canada Small Business Financing Program, which helps new companies access loans.
- Credit cards and lines of credit: Convenient but often carry high interest rates, so use cautiously.
- Angel investors: Wealthy individuals who provide funding and mentorship.
- Venture capital: Typically reserved for high-growth industries like tech and biotech.
- Grants and subsidies: Some government grants do not require repayment. Use the Business Benefits Finder to discover programs you may qualify for.
- Business incubators: These organizations provide resources, mentorship, and networking opportunities. They are especially helpful for start-ups in technology and innovation sectors.
Pros and Cons of Financing Sources for Start-ups

Choose a Commercial Space

When you choose to create business in Canada in a physical place, buying or renting is one of the first choices. This choice will be determined by your budget, business model and long-term goals.
Location is essential to retailers and service-based companies as it influences visibility and availability to customers. With technology companies or consultancies, remote working can be a cheaper option.
In choosing a space, take into consideration staff, supplier, and client accessibility and possible renovation expenses. In case you are renting, you should always have your lease agreement reviewed by a lawyer to ensure you know what is expected of you.
The Government of Canada's guide on planning your business location indicates the need to protect your investment. Whether you rent or purchase, ensure that your business assets are insured.
The selection of a well-planned location enhances your business's credibility in registering a business in Canada and offers stability for growth.
Hire Employees

You might need to recruit employees as your company grows. Recruitment represents one of the most challenging entrepreneurial activities, particularly when a labour shortage occurs. It will not hurt to slow down and get it right the first time.
Tips for Hiring Your First Employee
- Prepare a job description, which specifies duties, skills and qualifications.
- Advertise the position on job boards, social media, and in your network.
- Only shortlist and interview those candidates who fit your criteria.
- Compare skills, experience, and cultural fit required using a checklist.
- Write interview questions that will investigate background and expertise.
- Request job applicants to provide examples of work they would do.
- Check references and then make the final decision.
- Present a written offer letter with regard to compensation, hours, benefits and vacation.
After the candidate accepts, you have to take subscriptions to the payroll deductions such as Canada Pension Plan (CPP), Employment Insurance (EI) and income tax. The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) offers step-by-step instructions on how to establish payroll accounts.
One of the most effective methods to open small business in Canada on a sound basis is to hire well, since good employees will determine your growth and success in the long term.
Grow Your Business

Starting your business is not enough. The actual problem is that it is hard to manage day-to-day activities and also be in control of the future. Most businesses do not survive during the first year, as they cannot balance between growth and stability.
The important parameters to consider are:
- Cash flow management: Anti-shortages by forecasting cash inflows and outflows. You can plan with the help of a good cash flow calculator.
- Time management: Build systems that help you to work on your business (strategy, marketing, growth), and not just in your business (day-to-day tasks).
- Scalability: Early put measures in place to ensure that expansion will not cripple your operations.
The Government of Canada’s Business Planning Guide offers resources to help entrepreneurs forecast and organize growth. Using such resources is one of the clearest paths if you’re wondering how to setup a firm in Canada step by step.
FAQs About Company Registration in Canada
1. What is company name registration Canada and why is it important?
Company name registration Canada ensures that your business name is legally recognized and protected. Registering helps to avoid the use of the same name or a confusingly similar name by others. This will also gain credibility among customers, investors and banks, as your name will be attached to your official records.
2. How do I register a business in Ontario Canada?
To register a business in Ontario Canada, you must file through ServiceOntario, the provincial portal for business registration. You will need to select the form of business (solo, partnership or corporation), register the business name, and pay a small fee. Ontario will also permit you to do this online within a few steps.
3. What does establishing a business in Canada involve?
Establishing a business in Canada requires more than just registration. You will be required to choose a legal structure, register taxes, licences and permits, safeguard your intellectual property, and establish banking. A lot of entrepreneurs also develop an elaborate business plan and employ professionals such as accountants or lawyers to mentor them.
4. How to start a business in Canada from USA?
If you’re a U.S. resident wondering how to start a business in Canada from USA, the process is similar to Canadian residents but with some added steps. You might be required to incorporate as an extra-provincial corporation, have a Canadian representative or director and be subject to cross-border tax regulations. Provincial and federal governments give elaborate instructions to foreign investors and entrepreneurs.








