Copyright and trademarks are the legal mechanisms to protect inventions and brands. Understanding the distinctions between copyright vs trademark will help you to determine the ways that will help protect your property moving forward. Copyright and trademark are different, but each protects certain aspects of creativity and trade.
Copyright refers to the exclusive rights owners have over their original literary, musical, and artistic works. Because it gives authors the right to how their works should be utilized and sold, they will have the benefits of their creation. On the other hand, trademarks are intended to cover any recognizable symbols, such as logos, names, or slogans, which make it easy for consumers to distinguish between different commodities or services.
It is essential to differentiate between a copyright and a trademark since the two are different legal ways in the field of intellectual property. This understanding assists individuals and companies in seeking an adequate form of protection based on their needs in order to protect their creative works and brand identities.
Table of contents.
- Introduction
- What is copyright?
- Developing Copyright
- What is a trademark?
- Developing a trademark application and reviewing it
- Key differences between copyright and trademark
- When to use copyright vs. trademark
- Legal considerations
- Conclusion
What is Copyright?

Copyright is a form of legal protection afforded to creators of original artistic and intellectual works in literature and art, including books, music, movies, and paintings. The law empowers creators to determine in what manner the works they create should be employed as well as to assert their rightful claims for rewards and recognition of their work. Copyright is set up to foster creativity and development by giving sole rights to individuals who generate content.
Types of Works Protected by Copyright
Copyright applies to literary works (novels, poems), musicals, dramatic plays or ballets, choreography, paintings, drawings, sculptures, movies, and sound fixes. It also extends to software and architectural designs.
How Copyright is Obtained
It is said that copyright is acquired when an original work is created and exists in a real medium of expression where the work is copied or recorded. However, the protection of a work is automatic under copyright law, and registration of the work with a copyright office can be of legal advantage in many cases, such as the ability to sue for statutory damages.
Duration of Copyright Protection
As a general rule, copyright is acquired during the life of the author and seventy years thereafter. Collective works last for 70 years after the death of the last surviving author of the work. Photographic works made for hire and other works where the author is unknown have a protection term of ninety-five years from publication or one hundred and twenty years from creation, whichever is lesser.
Examples of Copyrighted Works
Some examples include a book that has become popular among readers, a song sung by a favorite artist, a movie that is much loved, software, and a snapshot taken by a photojournalist. All of these works are copyrighted, which means that the owners have exclusive rights over their application and utilization.
Developing Copyright
Copyright is developing based on three key components:
- Originality: The work must be original in the sense that the author has produced it on his own, and it would have a measure of creativity.
- Authorship: Among other things, it must be a work of authorship, so it can fall into categories like literary, musical, artistic, and others.
- Fixation: The work has to be embodied in a physical medium, either written, recorded, or stored in a place that allows people to perceive it or reproduce it.
What is a Trademark?

A trademark is any sign that is capable of being used to mark the origin of goods or services of one business from those of another one. It is the use of words, logo designs, symbols, and slogans. The role of a trademark is to act as a shield to brand names and assure that customers can easily distinguish providers of products or services..
Types of Trademarks (Word Marks, Logos, Slogans, etc.)
There are several types of trademarks:
- Word marks ( slogans such as Nike)
- Logos (graphics such as the bitten apple symbolizing Apple)
- Slogans (mottos such as ‘Just Do It’).
How Trademark is Obtained
The process of how to trademark your business name involves seeking registration from the appropriate trademark office. This involves filing the trademark application together with the trademark itself, a statement of the goods and services in relation to which the trademark has been used or is intended to be used in commerce, and proof of use or intent to use it in commerce.
Duration of Trademark protection can be forever provided the owner continues to use the trademark in the course of trade, and it remains unregistered. In most countries, trademark rights are valid for a specific period of time, and the owners must renew the registration and continue using the trademark.
Examples of Trademarks

Examples of famous trademarks are the McDonald’s golden arches, the Coca-Cola trademark, and the Starbucks trademark. These trademarks are protected in order to maintain proper identification of the owners of the respective marks and to avoid the use of similar marks by other parties that may cause confusion among consumers.
Developing a Trademark Application and Reviewing it

A trademark application is a process of filing a formal application to register a trademark through the trademark office in a particular country, such as the United States Trademark Office (USPTO). It contains the trademark itself in its natural form, information about the goods or services that the trademark identifies, and relevant evidence of its usage or the intention to use in commerce.
In the life cycle of a trademark application after submission, the trademark office evaluates the application to ensure compliance with legal frameworks. They search for any conflicting marks and verify that the mark chosen is sufficiently different from other related marks.
The application is then published for opposition, which means that other people can object to it if the application has passed the review. If there is no opposition within a period of 30 days from the publication of the trademark, then the trademark is registered, thereby affording the owner the legal right.
Key Differences (Copyright vsTrademark)
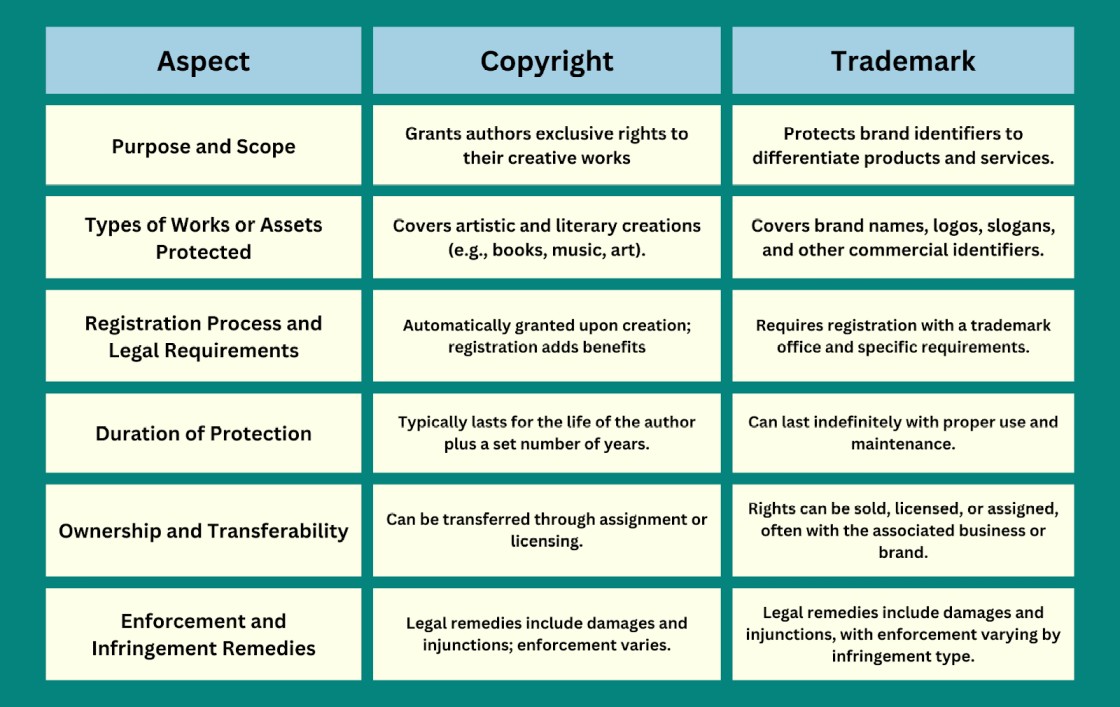
When to Use Copyright vs Trademark

Deciding Based on the Nature of the WorkThe selection of a copyright or trademark depends on whether it is a creative work to protect or an identifier of origin. Copyright law applies to instances involving artistic and literary creations, whereas trademark protection concerns brand names and logos.
Legal Considerations (Copyright vs Trademark)

International Perspectives on Copyright and Trademark
A discussion of how the legal protection for copyright and trademarks vary from country to country and why foreign laws on intellectual property should be carried out in the international business environment.
Consequences of Infringement
This will outline the potential consequences of intentional acts of copying or using copyrighted/trademarked material, along with penalties and possible legal actions.
How to Protect Your Intellectual Property
Registration and monitoring may be undertaken to ensure that your intellectual property rights are properly protected and what action should be taken in case of infringements.
Conclusion:
Copyright protects creators by giving them exclusive control over their creations. It also promotes further innovation by rewarding the creators of these works.
Trademark legislation safeguards such elements as logos and mottos to guarantee the identity of enterprises and companies. Whereas copyright applies itself to any creative work, trademarks require protection by formal registration to prevent identity theft. Legal protection and industrial protection are important as they have different roles in the protection of rights and the prevention of infringement. Understanding when to employ each is crucial for creators and companies to correctly safeguard their ideas. For additional protection against identity theft, Cybernews experts recommend reading their article on identity theft protection services. Understanding the best tools available can help individuals and businesses safeguard sensitive information from fraud and misuse.








